
All of the businesses records but be changed into the new software's type. In businesses, many times applications are upgraded. You have taught the computer to do something only by doing it once. Your computer does faster what you could do more tediously. If it can't read it though- perhaps in the future, you can correct it by dictating your letters instead. With the pen that accompanies your silicon note pad you can write a little note to yourself which magically changes into computer text if desired.

Cursive or Print can be recognized by notepad sized devices. This implication of AI in Personal computers is still very crude but it does work. You tell the computer to do what you want without it having to learn your voice. And their ease of use comes from their use of AI. We use PCs more not because they do more or are faster but because they are getting so much easier to use. Even with all the abuse we give today's PCs, they still plug away to make us happy. Who else would care to tell you that you have a business appointment scheduled at 8:35 and 28 seconds and would notify you about it every minute till you told it to shut up. Who else would go surfing with you on short notice- even if it is the net. From Macros to Voice Recognition technology, PCs are becoming our talking buddies. Not only are today's PCs becoming more powerful but AI influence is showing up in them. Īpple Computers may not have ever been considered as the state of art inĪrtificial Intelligence, but a second look should be given. Programming, therefore, is at a higher level than in them imperative languages. The advantage of declarative languages is that programs written in them are closer to the program specification. Whereas imperative languages give the computer a list of instructions to execute in a particular order, declarative programming describes to the computer a set of conditions and relationships between variables, and then the language executor (an interpreter or compiler) applies a fixed algorithm to these relations to produce a result. FORTRAN, Formula translation developed at IBM starting in 1954, was a compiled language that allowed named variables complex expressions, subprograms, and many other features now common in imperative languages.ĭeclarative programming languages stand in contrast to imperative languages. In these languages, instructions were very simple. The earliest imperative languages were the machine languages of the original computers. Imperative programs are a sequence of commands for the computer to perform. Imperative languages describe computation in terms of a program state and statements that change the program state. They all fall into two major categories: imperative languages and declarative languages. High-level programming languages are more complex than assemblers and much more complex than machine languages.
In fact, the first assembler was simply a system for representing machine instructions with simple mnemonics.īut most often the term programming language refers to high-level languages, such as BASIC, C, C++, COBOL, FORTRAN, Ada, Pascal, etc.
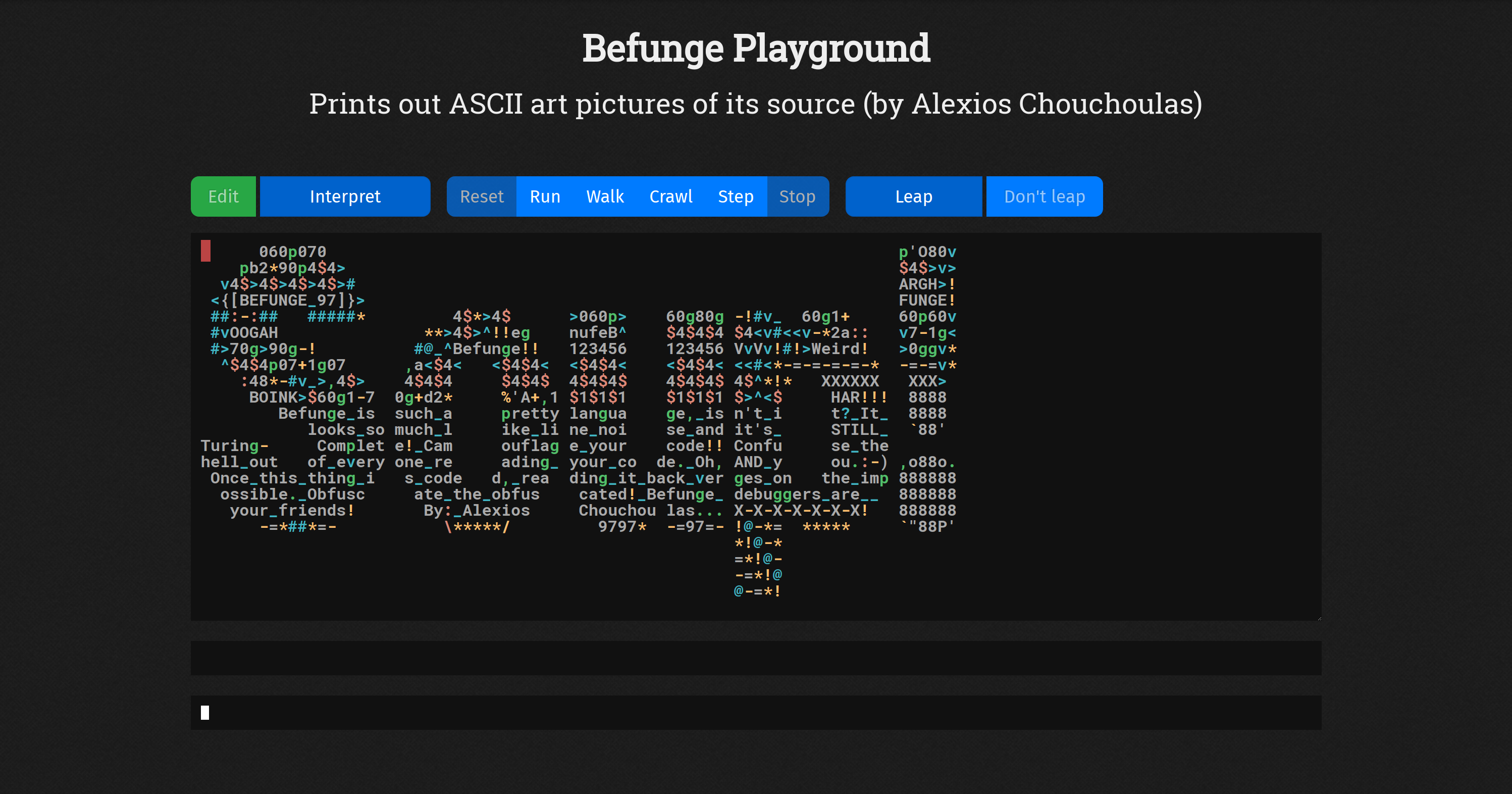
Lying between machine languages and high-level languages are languages called assembly languages.Īssembly languages, or assemblers are similar to machine languages, but they are much easier to program in because they allow a programmer to substitute names for numbers: ones and zeros and enable them to use meaningful names for instructions. Each different type of CPU (Central Processing Unit) has its own unique machine language. They consist entirely of numbers, and only numbers, - memory addresses and operation codes.

They are the least complex and the closest to computer hardware programming languages. Machine languagesare the languages that the computer actually understands. Each language has a unique set of keywords (words that it understands) and a special syntax for organizing program instructions. Programming language is a composition of vocabulary and set of grammatical rules for instructing a computer to perform specific tasks.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
